Jentic MCP + Visual Studio Code
Goal — In a few minutes, you’ll enable Jentic MCP tools in Visual Studio Code, allowing you to find, inspect, and run external APIs directly in your coding workflow.
What you’ll get
With Jentic MCP configured in Visual Studio Code, you'll gain access to powerful tools:
| Tool available in Visual Studio Code | What it does |
|---|---|
| /search_apis | Type what you need (e.g., "Send Discord Message", "Find New York Times Articles") and MCP lists matching APIs. |
| /load_execution_info | Click any result to view its full spec (URL, parameters, auth requirements). |
| /execute | Fill-in the parameters and run the API or workflow – response appears in the chat. |
Before you start
Ensure you have the following installed and configured:
| You need | Why | Quick install |
|---|---|---|
| Python ≥ 3.11 | Required for uv/uvx and Jentic CLI. | python.org |
| VS Code (latest) | The editor where you'll use MCP. | code.visualstudio.com |
| GitHub Copilot | MCP servers extend the agent capabilities of Copilot Chat. | Marketplace |
| uv / uvx runtime | Launcher that runs the Jentic MCP server. | Install with pip: pip install uv (any OS) or with Homebrew (macOS): brew install uvIf you have trouble with uvx, see Making Visual Studio Code See uvx below. |
1. Get Your API Key (if you don't have one already)
To use the Jentic SDKs or MCP Plugin, you must obtain your API key. The easiest way is using the Jentic CLI. You can optionally include an email address for higher rate limits and for early access to new features.
pip install jentic
jentic register --email '<your_email>'
This will print your API key and an export command to set it in your environment:
export JENTIC_UUID=<your-api-key>
Alternatively, you can use curl to register and obtain your API key:
curl -X POST https://api.jentic.com/api/v1/auth/register \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"email": "<your_email>"}'
2. Configure MCP in Visual Studio Code (Global recommended)
The easiest way is to set this up globally so Jentic works in all your projects:
- Open the Command Palette (macOS ⌘⇧P / Windows/Linux Ctrl+Shift+P, or F1).
- Run MCP: Open User Configuration — this opens/creates your global
mcp.json.
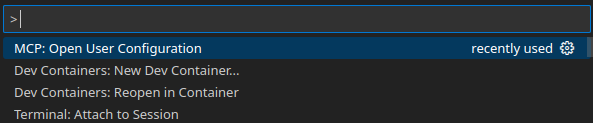
- Paste the JSON and replace
<your-api-key>, then Save:
{
"servers": {
"jentic": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--from",
"git+https://github.com/jentic/jentic-sdks.git@main#subdirectory=mcp",
"mcp"
],
"env": {
"JENTIC_UUID": "<your-api-key>"
}
}
}
}
Can't find "MCP: Open User Configuration"? Try updating VS Code (macOS: gear icon → Check for Updates) or see the FAQ below.
(Optional) Per‑project setup
If you want to share config with a repo/team or keep it project‑scoped, create .vscode/mcp.json in your workspace instead. You can also run MCP: Add Server and choose Workspace to have VS Code create/populate the file for you.
Note: Cursor and VS Code have separate user profiles, but workspace config (
.vscode/mcp.json) works across both editors.
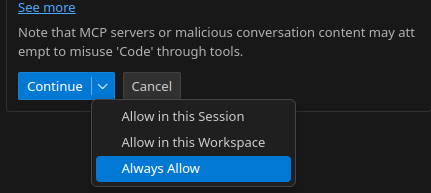
3. Stop repeated permission prompts
When Copilot wants to run a Jentic tool, VS Code asks for permission. Click Continue ▾ and choose Always allow – never ask again (all sessions/workspaces).
4. (Optional) Add API keys and environment variables
Steps for additional API keys
Some APIs returned by /search_apis → /load_execution_info will list required tokens or base‑URLs. Add them once and VS Code passes them automatically.
- Open the same
mcp.jsonfile. - Insert or update the
envblock inside thejenticserver. - Save the file (you may need to restart VS Code).
Full example after adding keys
{
"servers": {
"jentic": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--from",
"git+https://github.com/jentic/jentic-sdks.git@main#subdirectory=mcp",
"mcp"
],
"env": {
"JENTIC_UUID": "<your-api-key>",
"DISCORD_BOTTOKEN": "<your-discord-bot-token>",
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "<your-openai-api-key>"
}
}
}
}
Security tip: The
mcp.jsonfile is plain text. Ensure it's stored securely, especially if it contains sensitive API keys.
5. Use MCP tools in Agent Mode
- Open the Chat view (Windows/Linux: Ctrl+Alt+I; macOS: Control–Command–I). Switch to Agent mode.
- When prompted to trust the Jentic server, choose Always allow (or Current workspace) to avoid future prompts.
- Click the Tools icon to see available tools, or reference a tool in your prompt with
#tool. -
Enter a prompt. Copilot will automatically invoke tools as needed, asking for your confirmation before running them.
You can also directly reference a tool in your prompt by typing
#followed by the tool name (e.g.,#search_apis).
6. If something doesn’t work
| What you see / Problem | Try this |
|---|---|
| Jentic MCP tools not showing in VS Code | Check your .vscode/mcp.json file for syntax errors (e.g., missing commas, incorrect brackets). Ensure VS Code was fully restarted after any changes. Check the server logs by running MCP: List Servers, selecting jentic, and choosing Show Output. |
| "command not found: uvx" (in logs or error) | uvx is not in a path VS Code can see. See "Making Visual Studio Code See uvx" below for details. |
| API calls fail (e.g., 401/403 errors) | The API likely requires authentication. Use /load_execution_info to check its requirements, then add necessary API keys/tokens to the env block in the config file (see Step 3). Restart VS Code. |
| "MCP: Open User Configuration" doesn't appear in Command Palette | macOS users: Update VS Code first (gear icon → Check for Updates). Alternative: Manually create the file at ~/Library/Application Support/Code/User/mcp.json (macOS), %APPDATA%\Code\User\mcp.json (Windows), or ~/.config/Code/user/mcp.json (Linux). |
Making Visual Studio Code See uvx
VS Code is a GUI app; it doesn’t read your shell profile, so binaries added to PATH in .zshrc/.bashrc may be invisible. Choose one of these options:
Option A – Homebrew / System package (macOS & Linux)
- Homebrew (macOS) or your distro’s package manager / a
sudo pip install uvdropsuvxsomewhere VS Code already looks:/usr/local/binon Intel Macs & most Linux distros/opt/homebrew/binon Apple Silicon
If which uvx returns one of these paths, you’re good – skip this section.
Option B – pip / pipx / pyenv (user-local installs)
If uvx lives in a user-local directory, expose it via a symlink (macOS/Linux) or by adding the folder to PATH (Windows).
- macOS / Linux – symlink
sudo ln -sf "$(which uvx)" /usr/local/bin/uvx # use /opt/homebrew/bin on Apple Silicon sudo ln -sf "$(which uv)" /usr/local/bin/uv - Windows – PATH
- Locate the folder containing
uvx.exe(e.g.%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python311\Scripts). - Add that folder to Path in Environment Variables….
- Restart VS Code (and any open terminals).
- Locate the folder containing
Option C – Hard-code the full path
Alternatively, you can skip creating symlinks and directly specify the full path to the binary in the configuration file.
For more details on managing MCP servers in VS Code, see the Official Visual Studio Code MCP server docs.
Additional FAQ
Q: Do Cursor and VS Code share MCP configurations?
Cursor and VS Code have separate user profiles, so global configurations don't sync between them. However, workspace config (.vscode/mcp.json) works across both editors.
Q: Should I use global or workspace configuration?
- Global (recommended): Use when you want Jentic available in all projects
- Workspace: Use when sharing config with a team or keeping it project-specific